Minimum Energy Control of Lattices
The control energy of lattices can provide an estimate of the control in complex networks.
The control energy of lattices can provide an estimate of the control in complex networks.
A brief overview of my work in generating graphs with desired symmetries.
Afroza Shirin, Isaac Klickstein, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2017
We hypothesized that the large control energy that arises when applying the minimum energy control to a complex network is due to the implicit requirement of perfect accuracy. By relaxing this requirement, we show there is an exponential reduction in control energy.
Download here
Isaac Klickstein, Afroza Shirin, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Nature Communications, 2017
My first investigation into the optimal control of networked systems. The main focus was on the role of the number of control targets.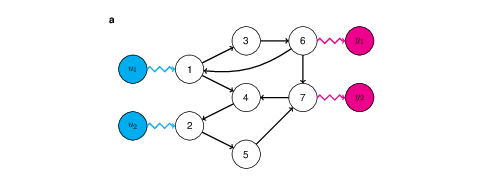
Download here
Isaac Klickstein, Afroza Shirin, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Physical Review Letters, 2017
We use the solution of the minimum energy control problem for linear systems to derive a piece-wise controller to overcome the limitations of the nonlocality introduced by linearization.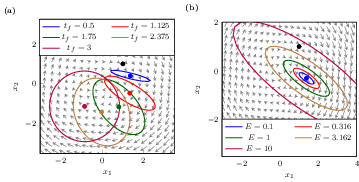
Download here
Ishan Kafle, Sudarshan Bartaula, Afroza Shirin, Isaac Klickstein, Pankaz Das, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2018
We specialized the minimum energy control problem to the case that there are external signals which must countered.
Download here
Isaac Klickstein and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2018
This is an improved version of the algorithm to generate graphs with symmetry that we previously published.
Download here
Isaac Klickstein and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2018
This is an improved version of the algorithm to generate graphs with symmetry that we previously published.
Download here
Isaac Klickstein, Ishan Kafle, Sudarshan Bartaula, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2018
This was my first attempt at using simple graph models to explain the enormous variance of control energy when holding the number of driver nodes and the number of target nodes constant even over the same graph.
Download here
Isaac Klickstein and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2018
To investigate the single driver single target control problem on a network, the exact solution of the differential Lyapunov equation is derived for an infinite path graph which is shown to be a good approximate value for sparse networks. We also introduce a corrective factor by computing the controllability Gramian of a model to represent the role of redunant paths.<div style='text-align:center'>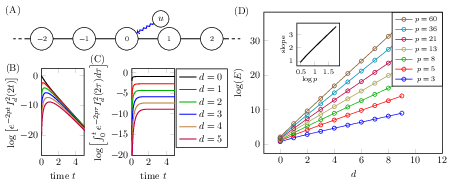 </div>
</div>
Download here
Isaac Klickstein and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in 2018 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), 2018
The controllability Gramian of hyper-cubic graphs is derived analytically to investigate the role of graph density in the reduction of control energy.
Download here
Afroza Shirin, Isaac Klickstein, Song Fend, Yen Ting Lin, William Hlavacek, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Scientific Reports, 2019
Numerical optimal control techniques are applied to a recently developed model of cellular autophagy to determine promising multi-drug therapies. We found surprising drug combinations capable of up-regulating or down-regulating autophagy where each drug alone was unable to perform the task.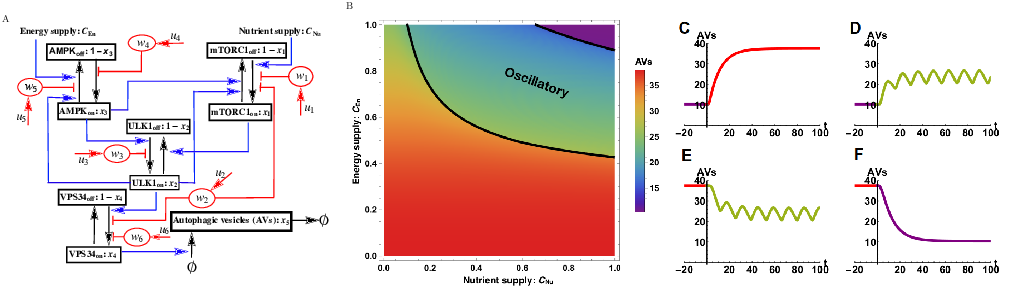
Download here
Afroza Shirin, Fabio Della Rossa, Isaac Klickstein, John Russell, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in PLoS ONE, 2019
Numerical optimal control techniques are applied to the FDA approved model for in silico diabetes treatment testing. We both recover the pulsatile solution representing the well-known treatment of injecting a shot of insulin roughly 30 minutes before eating as well as develop potential treatment schedules when both insulin and glucagon are available.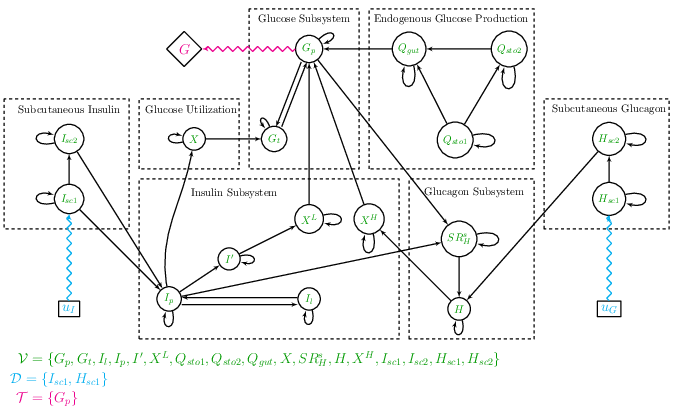
Download here
Isaac Klickstein, Louis Pecora, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2019
The consensus problem is investigated for networked systems which exhibit graph symmetries. By using a block diagonalizing transformation that makes explicit symmetric and non-symmetric motion, we show that consensus is possible even when the entire system is unstable.
Download here
Afroza Shirin, Isaac Klickstein, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2019
Reservoir computers are a type of learning algorithm designed to learn dynamical systems. We derive a class of Lyapunov functions to ensure the reservoir computer remains stable while also demonstrating that reservoir computers which are barely stable are the best at representing unknown dynamical systems.
Download here
Isaac Klickstein and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Automatica, 2020
This was the culmination of the analytic solution of lattice networks. The solution is derived in terms of integrals whose expression in terms of elementary functions is unlikely though.
Download here
Fabio Della Rossa, Louis Pecora, Karen Blaha, Afroza Shirin, Isaac Klickstein, and Francesco Sorrentino
Published in Nature Communications, 2020
In this work I developed the method to determine symmetries in multilayer networks.
Download here